What is Database ?
- it's a collection of data
- can access and manipulate data
- computerised data with an accessible interface
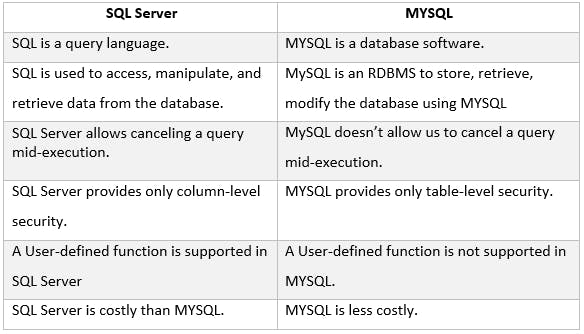
SQL VS MYSQL
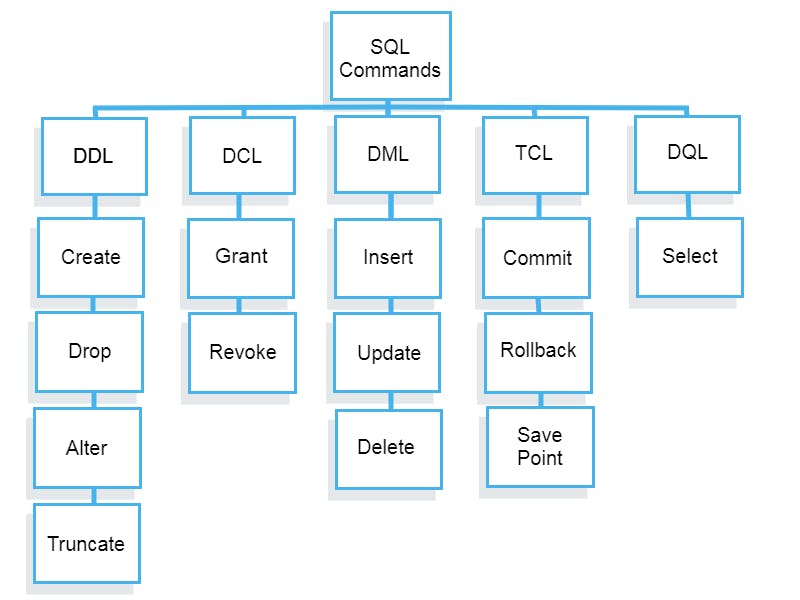
SQL Command Types : DDL, DML, DCL, TCL, DQL
-> DDL – Data Definition Language
-> DQl – Data Query Language
-> DML – Data Manipulation Language
-> DCL – Data Control Language
-> TCL - Transaction Control Language
SQL Operations
Create
create table table_name( column_name datatype auto_increment not null, column_name datatype not null default "default val", column_name datatype null, primary key(column_name) );Read
select * from table_nameInsert
insert into table_name(column1,coumn2) values (col1_val,col2_val), (col1_val,col2_val), (col1_val,col2_val);Update
update table_name set col_name = updated_val where condition;Delete
Delete command is used to delete existing records in a tabledelete from table_name where condition;Drop
Drop command destroys the objects like an existing database, table, index, or viewdrop database db_name drop table table_nameTruncate
Truncate command deletes the data inside a table, but not the table itself.truncate table table_name;
SQL Clauses
- Where
select * from table_name where condition;
- Having
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
GROUP BY column_name(s)
HAVING condition
ORDER BY column_name(s);
Query Example :
SELECT COUNT(CustomerID), Country
FROM Customers
GROUP BY Country
HAVING COUNT(CustomerID) > 5;
Distinct
select distinct(col) from table_name where condition;Order By
SELECT col from table_name where condition order by col(according to which you need to sort) desc;Aliases(Using as)
select cat_id as id from cats where cat_id=age;Limit
select col_name from table_name order by col_name desc limit number; select col_name from table_name order by col_name desc limit skip-result, number;
SQL String Functions
Concat
select concat(col1,' ',col2) from table_name where condition;Substring
select substring(col,start_idx,end_idx) from table_name where condition; select substring(col,idx) from table_name where condition; -> this will return characters after idx in string select substr(col,start_idx,end_idx) from table_name where condition; -> this will also work same as substringReplace
select replace(col, what to replace in col, Val of replacement) as name from table_name where condition;Reverse
select reverse(col) as reversedStrings from table_name where condition;Char_Length
select char_length(col) as colDataLength from table_name where condition;Upper and Lower
select upper(col) as upperCase from table_name where condition; select lower(col) as lowerCase from table_name where condition;Like
'_' = 1 character '%' = any character '\' = exactly before this and exactly after this match will returnSELECT * from table_name where col_name like '%he%'; -> return if it founds he anywhere in col_val SELECT * from table_name where col_name like 'he%'; -> return if col_val start with he SELECT * from table_name where col_name like '%he'; -> return if col_val end with he SELECT * from table_name where col_name like '__'; -> return if col_val has only 2 characters SELECT * from table_name where col_name like '%\_%' -> return val like 10% or fetch_data etc...
SQL Aggregate Functions
Count
select count(col_name) from table_name;Group By
select col_name, count(*) from table_name where condition group by col_name -> returns 1st row of every group and number of rows every group containsMin And Max
select min(col_name) from table_name; select max(col_name) from table_name;Sum
select sum(col_name) from table_name group by col_name;Average - AVG
select avg(col_name) from table_name group by col_name;
SQL Data Types
Char and Varchar
Char→ fixed length (0 to 255) → if length is 10 then it will store exact 10 characters Varchar→ varied length (0 to 255)store : "coder" in char(8) => "coder " in varchar(8) => "coder"Decimal
Decimal(val1,val2) val1 -> max digits you can store val2 -> num of digits right after decimal pointFloat And Double
Float data can hold 8 bytes, or 15 places after the decimal point. Double data is similar to float, except that it allows for much larger numbersDATE & TIME && DATETIME
DATE -> 'YYYY-MM-DD' format (stores only date) TIME -> 'HH:MM:SS' format (stores only time) DATETIME -> 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'CURDATE, CURTIME AND NOW
CURDATE -> current date CURTIME -> current time NOW -> current datetimeFormatting Dates
DAY(), DATEADD(), DAYNAME(), DAYOFYEAR(), DAYOFWEEK(), DATE_FORMET(), DATEDIFF(date1,date2),TIMESTAMPS
TIMESTAMPS() -> Less space compare to DATETIME()
Logical Operators
Not Equal (≠)
select * from table_name where col_val != val;Not Like
select * from table_name where col_val not like val;Greater Than And Less Than
select * from table_name where col_val > val; select * from table_name where col_val >= val; select * from table_name where col_val < val; select * from table_name where col_val <= val;And
select * from table_name where col_val=val and col_val=valOr
select * from table_name where col_val=val or col_val=valBetween
select * from table_name where col_val between val1 and val2;In
select * from table_name where col_val in (val1,val2,val3);Not In
select * from table_name where col_val not in (val1,val2,val3);Case Statements
Query Example : SELECT OrderID, Quantity, CASE WHEN Quantity > 30 THEN 'The quantity is greater than 30' WHEN Quantity = 30 THEN 'The quantity is 30' ELSE 'The quantity is under 30' END AS QuantityText FROM OrderDetails;
Relationships
→ One to One Relationship
→ One to Many Relationship
→ Many to One Relationship
→ Many to Many Relationship
Joins
Full Join
=> Returns all the records from both tables SELECT * FROM table1_name,table2_name;Inner Join
=> Returns common records from both tables SELECT * FROM table1_name inner join table2_name on table2_name.col_name = table2_name.col_name;Left Join
=> Returns all the records from left table and matching one from right table SELECT * FROM table1_name left join table2_name on table2_name.col_name = table2_name.col_name;Right Join
=> Returns all the records from right table and matching one from left table SELECT * FROM table1_name right join table2_name on table2_name.col_name = table2_name.col_name;
Window Functions
- partition by
select *, aggregate_function(col_name) over(partition by col_name order by col_name desc) from table_name; Rank, Row_Number, Dense_Rank window functions
select *, row_number() aggregate_function(col_name) over(partition by col_name order by col_name desc) as row_num, rank() aggregate_function(col_name) over(partition by col_name order by col_name desc) as rank_val, dense_rank() aggregate_function(col_name) over(partition by col_name order by col_name desc) as dense_rank_val from table_name;Lead
select *, lag(col_name, 1) over(order by col_name) as pre_val from table_name;Lag
select *, lead(col_name, 1) over(order by col_name) as next_val from table_name;Frame Clause In Window Functions
select *,
aggregate_function(col_name) over(order by col_name rows between n preceding and m following) as prev_current_and_next
from table_name;
select *,
aggregate_function(col_name) over(order by col_name rows between n preceding and current row) as previous_and_current
from table_name;
select *,
aggregate_function(col_name) over(order by col_name rows between current row and m following) as current_and_next
from table_name;
select *,
aggregate_function(col_name) over(order by col_name rows between unbounded preceding and current row) as current_to_firstRow_upwards
from table_name;
select *,
aggregate_function(col_name) over(order by col_name rows between current row and unbounded following) as current_to_lastRow_downwards
from table_name;
select *,
aggregate_function(col_name) over(order by col_name rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following) as current_to_upwards_and_downwards
from table_name;
select *,
aggregate_function(col_name) over(order by col_name range between n preceding and m following) as diff_between_current_and_upwards_not_less_then_m_and_downwards_not_greater_then_m
from table_name;
Union and Union All
Union
select * from table_1
UNION
select * from table_2;
Union All
select * from table_1
UNION ALL
select * from table_2;
Views
=> virtual tables = used to hide some crucial data from database users
=> do not occupy any space
CREATE VIEW view_name as
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
Common Table Expressions
Syntex
with output as query;
Example
with dept_wise_salary as (select dept_id , sum(salary) as total_salary from amazon_employees group by dept_id)
------ Write a Query to generate numbers from 1 to 10 in SQL ------
with recursive generate_numbers as
(
select 1 as n
union
select n+1 from generate_numbers where n<10
)
select * from generate_numbers;
Triggers
=> Triggers are the SQL codes that are automatically executed in response to certain events on a particular table
create trigger [trigger_name]
[before | after]
{insert | update | delete}
on [table_name]
[for each row]
[trigger_body];
Query Example :
create trigger stud_marks
before INSERT
on
Student
for each row
set Student.total = Student.subj1 + Student.subj2 + Student.subj3, Student.per = Student.total * 60 / 100;
Stored Procedures
A stored procedure is a prepared SQL code that you can save, so the code can be reused over and over again.
So if you have an SQL query that you write over and over again, save it as a stored procedure, and then just call it to execute it.
You can also pass parameters to a stored procedure, so that the stored procedure can act based on the parameter value(s) that is passed.
CREATE PROCEDURE procedure_name
AS
sql_statement
GO;
EXEC procedure_name;
Query Example :
CREATE PROCEDURE SelectAllCustomers
AS
SELECT * FROM Customers
GO;
EXEC SelectAllCustomers;
